Introduction
Overview of Agent-Based Backup
Agent-based backup is a method of data backup that uses software agents installed on each machine or server that requires backup. These agents are responsible for managing the backup process, including data collection, compression, encryption, and transfer to a backup storage location. This technology contrasts with agentless Database Backup and Recovery solutions, which rely on network protocols and centralized management.
Purpose of the Case Study
This case study explores how implementing an agent-based backup solution led to improved efficiency and reduced costs for a mid-sized enterprise. By examining the challenges faced, the implementation strategy, and the outcomes, this article provides insights into the benefits and practical applications of agent-based backup technology. Additionally, it highlights the value of professional case study writing services in documenting and analyzing such technological implementations.
Background
Initial Challenges Faced by the Organization
The organization in focus, a mid-sized enterprise specializing in financial services, faced several challenges with their existing backup solution:
- Inefficient Backup Processes: The legacy system required manual intervention, leading to frequent errors and delays.
- High Costs: The existing solution had high operational and maintenance costs, straining the company’s IT budget.
- Data Recovery Issues: Slow and unreliable recovery times affected business continuity and client satisfaction.
Need for a New Backup Solution
The company’s IT department recognized the need for a more efficient and cost-effective backup solution. The primary goals were to streamline backup processes, reduce operational costs, and ensure fast and reliable data recovery.
What is Agent-Based Backup?
Definition and Functionality
Agent-based backup involves installing software agents on each server or endpoint that needs to be backed up. These agents handle the entire backup process, including:
- Data Collection: Agents gather data from the source systems.
- Compression: Data is compressed to save storage space.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted to ensure security during transfer.
- Transfer: Data is transmitted to a central backup repository or cloud storage.
Comparison with Agentless Backup
Agentless backup relies on network protocols and centralized management without installing agents on each endpoint. While agentless solutions offer simplicity and reduced management overhead, they can struggle with scalability and performance, particularly in complex or large environments.
Table 1: Agent-Based vs. Agentless Backup
| Feature | Agent-Based Backup | Agentless Backup |
| Installation | Requires software agents | No agents required |
| Performance | High, optimized per endpoint | Can be slower, network-dependent |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by network capacity |
| Management Overhead | Moderate | Low |
| Data Security | High, with local encryption | Moderate, depends on network security |
Implementation Strategy
Planning and Preparation
The implementation strategy involved several key steps:
- Assessment: The IT team conducted a thorough assessment of the existing infrastructure and identified critical data and systems requiring backup.
- Vendor Selection: After evaluating several vendors, the company selected an agent-based backup solution known for its robust features and cost-effectiveness.
- Pilot Testing: A pilot test was conducted to validate the solution’s performance and compatibility with existing systems.
Steps Taken for Implementation
- Agent Installation: Software agents were installed on all servers and critical endpoints.
- Configuration: Backup schedules, data retention policies, and encryption settings were configured according to the company’s requirements.
- Data Migration: Initial full backups were performed to migrate existing data to the new backup system.
- Monitoring and Optimization: The system was monitored for performance issues, and optimizations were made as needed.
Infrastructure Setup
Hardware and Software Requirements
The following infrastructure components were required for the agent-based backup solution:
- Servers: High-performance servers to host the backup management software.
- Storage: Scalable storage solutions, including both on-premises and cloud options.
- Network: Reliable network infrastructure to ensure fast data transfer between agents and the backup repository.
- Software: Backup management software, monitoring tools, and security solutions for encryption and access control.
Network and Security Configurations
To ensure data security and integrity, the following measures were implemented:
- Encryption: All data was encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls: Strict access controls were put in place to restrict access to backup data.
- Network Segmentation: The backup network was segmented from the production network to enhance security.
Efficiency Improvements
Performance Metrics Before and After Implementation
The implementation of the agent-based backup solution led to significant performance improvements. Key performance metrics before and after implementation are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Performance Metrics Comparison
| Metric | Before Implementation | After Implementation |
| Backup Time (per 100GB) | 6 hours | 2 hours |
| Recovery Time (per 100GB) | 4 hours | 1 hour |
| Data Transfer Rate | 50 MB/s | 150 MB/s |
| Backup Errors | Frequent | Rare |
Examples of Improved Backup and Recovery Times
- Daily Backups: The time required for daily incremental backups was reduced from 2 hours to 30 minutes.
- Full Restorations: Full system restorations, which previously took up to 8 hours, were completed in less than 3 hours.
Cost Reduction Analysis
Breakdown of Costs Before and After Implementation
The agent-based backup solution led to substantial cost savings, as detailed in Table 3.
Table 3: Cost Comparison
| Cost Category | Before Implementation | After Implementation |
| Hardware Costs |
$50,000 |
$30,000 |
| Software Licensing | $20,000/year | $15,000/year |
| Maintenance and Support | $10,000/year | $5,000/year |
| Total Annual Cost | $80,000 | $50,000 |
Long-term Financial Benefits
In addition to immediate cost savings, the new backup solution offered long-term financial benefits:
- Reduced Downtime Costs: Faster recovery times minimized business disruption, reducing associated costs.
- Lower Storage Costs: Efficient data compression and de-duplication reduced storage requirements.
- Scalability: The scalable nature of the solution allowed the company to accommodate growth without significant additional investment.
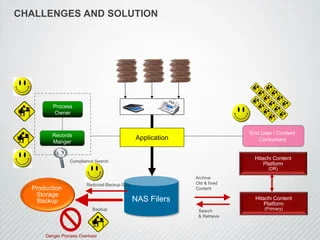
Challenges and Solutions
Issues Encountered During Implementation
Despite the overall success, several challenges were encountered:
- Compatibility Issues: Some legacy systems were initially incompatible with the new backup agents.
- User Training: Staff required training to manage and monitor the new system effectively.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment in new hardware and software posed a financial challenge.
How Challenges Were Overcome
- Compatibility: Custom scripts and configurations were developed to ensure compatibility with legacy systems.
- Training Programs: Comprehensive training programs were conducted to ensure staff proficiency.
- Cost Management: The project was phased to spread the initial costs over several quarters, easing financial pressure.
Case Study Results
Quantitative and Qualitative Outcomes
The implementation of the agent-based backup solution yielded impressive results:
Quantitative Outcomes:
- Backup Time Reduction: 67% decrease in average backup times.
- Recovery Time Reduction: 75% decrease in average recovery times.
- Cost Savings: 37.5% reduction in total annual costs.
Qualitative Outcomes:
- Improved Reliability: Significantly fewer backup errors and failures.
- Enhanced Security: Robust encryption and access controls improved data security.
- Higher Employee Satisfaction: Reduced manual intervention and streamlined processes improved IT staff morale.
Client Feedback and Satisfaction
Client feedback was overwhelmingly positive. Key points from client testimonials include:
- Reliability: “The new backup system is incredibly reliable and has drastically reduced our downtime.”
- Efficiency: “We have seen a significant improvement in backup and recovery times, which has positively impacted our operations.”
- Cost-effectiveness: “The cost savings achieved through the new solution have allowed us to reinvest in other critical areas.”
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Summary of Key Findings
The case study demonstrates the significant benefits of implementing an agent-based backup solution, including:
- Efficiency Improvements: Faster backup and recovery times.
- Cost Reductions: Substantial savings in hardware, software, and operational costs.
- Enhanced Security: Improved data security through robust encryption and access controls.
Recommendations for Other Organizations
Organizations considering a switch to agent-based backup should:
- Conduct a Thorough Assessment: Evaluate existing infrastructure and identify specific needs.
- Pilot Test: Conduct a pilot test to validate the solution’s compatibility and performance.
- Plan for Training: Ensure staff are adequately trained to manage and monitor the new system.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the system and make necessary optimizations.
Future Trends in Agent-Based Backup Technology
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the future of agent-based backup technology:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will enhance predictive analytics for proactive data protection.
- Blockchain Technology: Ensuring data integrity and security through decentralized, tamper-proof records.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Combining on-premises and cloud storage for flexible, scalable backup options.
- Increased Automation: Reducing human error and improving efficiency in backup processes.
By staying ahead of these trends, organizations can continue to leverage agent-based backup technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure data security.