Transformers are essential components in the world of electronics and electrical engineering. They are widely used to change the voltage of electricity, whether increasing or decreasing it. Among the different types of transformers, the transformer 1 1 is one of the most commonly used for specific applications.
In this article, we will explore the Transformer 1:1, its uses, construction, advantages, and various applications in both the electrical and electronic industries.
What is a Transformer 1:1?
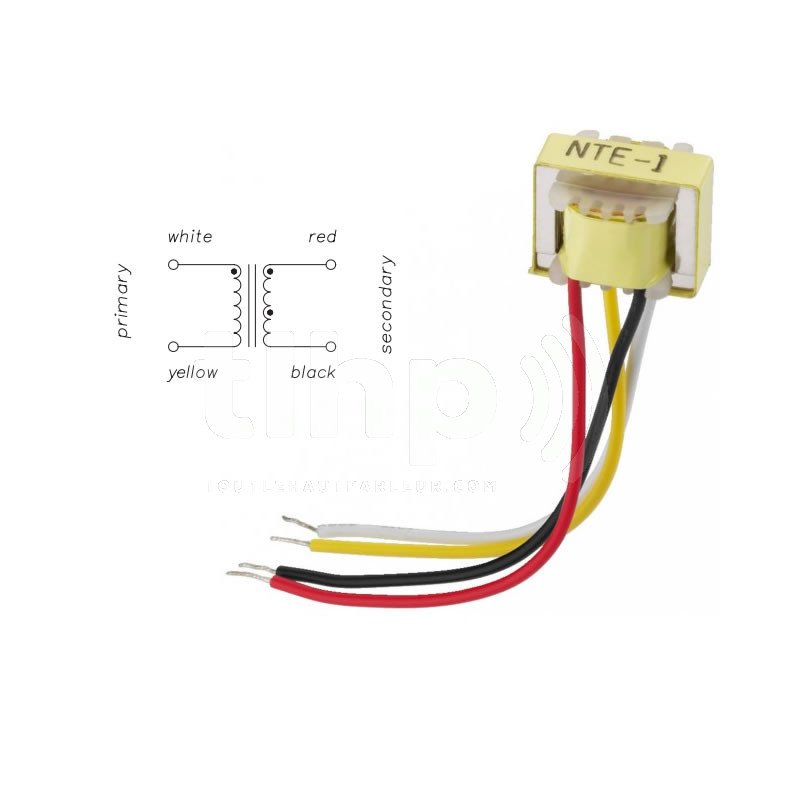
A Transformer 1:1 refers to a type of transformer with a 1:1 turns ratio. This means that the number of turns in the primary coil (input side) is equal to the number of turns in the secondary coil (output side). As a result, the voltage in the primary coil is transferred directly to the secondary coil without any increase or decrease.
In simple terms, a 1:1 transformer does not step up or step down voltage but is often used for other purposes such as isolation, signal transmission, or impedance matching.
Key Characteristics of a Transformer 1:1
There are several notable features that set a 1:1 transformer apart from other types of transformers:
No Voltage Transformation
Unlike step-up or step-down transformers, a 1:1 transformer keeps the voltage the same across both sides. The primary and secondary windings have equal numbers of turns, so the voltage at the input is the same as the voltage at the output.
Electrical Isolation
One of the primary benefits of a Transformer 1:1 is its ability to electrically isolate two circuits. This isolation helps protect sensitive equipment from voltage surges and noise from the power source, providing an additional layer of safety.
Impedance Matching
Another common use of a 1:1 transformer is for impedance matching. Impedance matching is crucial in applications like audio systems, telecommunications, and other signal transmission systems where power transfer efficiency is essential. A 1:1 transformer ensures that the impedance of the source and load match, which minimizes signal loss and maximizes efficiency.
Construction of a Transformer 1:1
Understanding the construction of a 1:1 transformer is essential for knowing how it functions and why it is so useful in various applications. A Transformer 1:1 consists of several basic components:
Primary Coil (Input Coil)
The primary coil is where the input electrical signal enters the transformer. In a 1:1 transformer, the number of turns in the primary coil is exactly the same as in the secondary coil. This ensures that the input voltage remains the same when transferred to the output.
Secondary Coil (Output Coil)
The secondary coil is where the output signal comes from. Since the 1:1 transformer has the same number of turns in both the primary and secondary coils, the voltage on the secondary side will be identical to the voltage on the primary side, but the current may vary based on the load.
Magnetic Core
The core of the transformer is usually made from ferromagnetic material such as silicon steel. The core helps to channel the magnetic field generated by the current in the coils, enabling efficient energy transfer between the primary and secondary windings. In a 1:1 transformer, the core size is generally designed to handle the required power levels without any significant losses.
Applications of a Transformer 1:1
Signal Isolation
One of the most common uses of a Transformer 1:1 is for signal isolation. This is especially useful in systems where electrical noise or ground loops can affect the performance of sensitive equipment. For instance, in audio equipment, a 1:1 transformer can help isolate signals between components like amplifiers and speakers, ensuring clean sound quality without unwanted interference.
Example: Audio Systems
In audio systems, 1:1 transformers are used to prevent hum and interference caused by ground loops. Ground loops occur when multiple pieces of equipment share a common ground, which can create noise. The Transformer 1:1 eliminates this by providing electrical isolation between the devices, ensuring that audio signals are clean and undistorted.
Impedance Matching
As mentioned earlier, a Transformer 1:1 is often used for impedance matching in electrical systems. Impedance matching is essential for ensuring maximum power transfer between the source and the load. In applications such as telecommunications, broadcasting, and audio systems, a 1:1 transformer helps maintain optimal signal strength and clarity.
Example: RF Applications
In radio frequency (RF) applications, 1:1 transformers are used to match the impedance between different parts of the system, such as antennas, transmitters, and receivers. This ensures efficient signal transmission and minimizes reflections, which can degrade performance.
Voltage Isolation in Power Systems
In power systems, Transformer 1:1 units are used to isolate circuits for safety purposes. This isolation prevents electrical faults from transferring between systems, protecting sensitive equipment from damage. These transformers are often used in control panels, industrial equipment, and electrical machinery where isolation from the main power supply is necessary.
Example: Industrial Equipment
In industrial applications, 1:1 transformers are often used to isolate control circuits from high-voltage power circuits. This ensures that the control systems remain protected from electrical surges or faults in the power supply, improving safety and reliability.
Advantages of a Transformer 1:1
Electrical Safety
One of the biggest advantages of using a 1:1 transformer is the added layer of electrical safety. By isolating circuits, these transformers prevent faults from propagating and help protect sensitive equipment from electrical surges, short circuits, or power spikes. This is especially important in industries such as telecommunications, medical devices, and industrial controls.
Efficiency
A 1:1 transformer allows for the efficient transfer of electrical power. Because the voltage remains the same, there is minimal energy loss in the form of heat, which ensures that the transformer operates with high efficiency.
Cost-Effective
Since Transformer 1:1 units are simple in design and don’t require complex voltage conversion, they are generally more cost-effective compared to step-up or step-down transformers. This makes them ideal for applications where voltage transformation is not necessary but isolation or impedance matching is still required.
How to Choose a Transformer 1:1
When selecting a 1:1 transformer, there are several factors to consider. These include:
Power Rating
The power rating of a 1:1 transformer indicates how much power it can handle without overheating or becoming inefficient. Make sure to choose a transformer with a power rating that suits your application.
Frequency Range
Different transformers are designed to operate over different frequency ranges. If you are using a 1:1 transformer in an audio or RF application, ensure that it is designed to handle the appropriate frequency range for your needs.
Size and Form Factor
The physical size of the 1:1 transformer is also an important consideration. It should fit within the space available in your equipment while still providing the necessary isolation or impedance matching.
Conclusion
The Transformer 1:1 is a versatile and essential component in both electrical and electronic systems. It provides efficient signal isolation, impedance matching, and voltage isolation without changing the voltage, making it ideal for various applications such as audio systems, RF devices, and industrial equipment. Understanding the construction, advantages, and applications of 1:1 transformers is crucial for anyone working in electronics or electrical engineering.
Whether you need to protect your sensitive equipment from electrical noise, match impedance in your circuits, or ensure safety in power systems, a Transformer 1:1 can provide the necessary functionality. By understanding the various aspects of this type of transformer, you can make informed decisions about its use in your specific applications.