Have you ever wondered about that distinctive maple syrup-like aroma wafting from certain spice blends? Chances are, you’ve encountered foenegriek, better known in English as fenugreek. This small, golden seed has been treasured for thousands of years across cultures, serving dual roles as both a culinary spice and a powerful medicinal herb.
Foenegriek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) belongs to the legume family and produces small, hard seeds that pack an impressive nutritional punch. While it might seem like just another exotic spice, this humble seed contains compounds that can support blood sugar control, boost milk production in nursing mothers, and even enhance athletic performance.
Whether you’re looking to diversify your spice cabinet or explore natural health remedies, understanding foenegriek’s rich history and science-backed benefits can help you make informed decisions about incorporating this versatile ingredient into your daily routine.
A Journey Through Time: The Rich History of Foenegriek
Foenegriek’s story begins in the Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia, where it has been cultivated for over 4,000 years. Ancient Egyptians valued the seeds so highly that they were found in King Tutankhamun’s tomb, believed to ensure prosperity in the afterlife.
The Romans gave fenugreek its Latin name, which translates to “Greek hay,” referencing its use as livestock fodder. However, they quickly discovered its culinary potential, incorporating the seeds into bread and wine preparations.
Traditional medicine systems across different cultures have long recognized foenegriek’s therapeutic properties. Ayurvedic practitioners in India have used it to support digestive health and enhance lactation in new mothers. Chinese medicine traditions employ fenugreek to strengthen the kidneys and support reproductive health.
During medieval times, Benedictine monks cultivated foenegriek in monastery gardens throughout Europe, using it to treat various ailments. This historical reverence laid the groundwork for modern scientific investigations into the seed’s remarkable health benefits.
Nutritional Profile: What Makes Foenegriek Special
Foenegriek seeds are nutritional powerhouses, containing an impressive array of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds. A single tablespoon (11 grams) of fenugreek seeds provides approximately 35 calories and delivers significant amounts of essential nutrients.
The seeds contain high levels of protein, fiber, and iron, making them particularly valuable for vegetarian and vegan diets. They’re also rich in magnesium, manganese, and copper, minerals that support bone health and metabolic function.
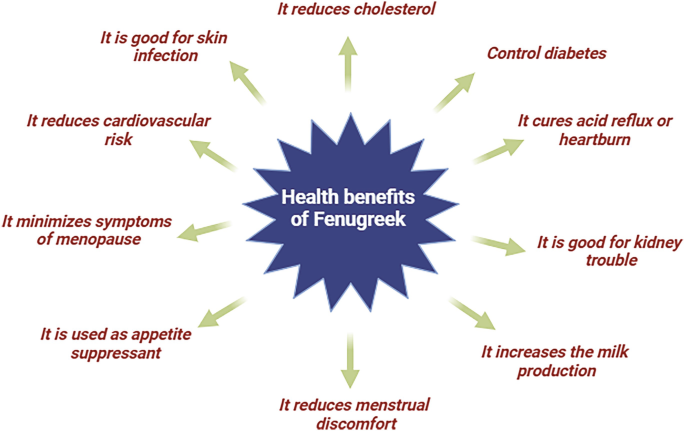
What sets foenegriek apart from other seeds is its unique compound profile. The seeds contain saponins, particularly diosgenin, which may help regulate cholesterol levels. They’re also rich in galactomannans, a type of soluble fiber that forms a gel-like substance when mixed with water.
Another notable component is 4-hydroxyisoleucine, an amino acid that appears to enhance insulin sensitivity. This compound, along with the seeds’ high fiber content, contributes to foenegriek’s blood sugar-regulating properties.
The distinctive maple syrup aroma comes from sotolone, a compound that becomes more pronounced when the seeds are roasted or cooked.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Foenegriek
Blood Sugar Management
Research shows that foenegriek can significantly impact blood glucose levels. The soluble fiber in the seeds slows carbohydrate absorption, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar after meals. Multiple studies have demonstrated that regular fenugreek consumption can improve glucose tolerance and reduce fasting blood sugar levels in both diabetic and pre-diabetic individuals.
The 4-hydroxyisoleucine content appears to stimulate insulin production when blood sugar levels are elevated, providing a natural mechanism for glucose regulation. This makes foenegriek particularly beneficial for people managing type 2 diabetes, though it should complement, not replace, prescribed medications.
Lactation Support
For centuries, new mothers have turned to foenegriek to boost milk production, and modern research validates this traditional use. Studies indicate that fenugreek supplementation can increase breast milk volume by up to 20% within just a few days of consistent use.
The galactagogue properties stem from the seeds’ phytoestrogen content, which may stimulate milk-producing hormones. Many lactation consultants recommend fenugreek as a natural alternative to pharmaceutical galactagogues, though nursing mothers should consult healthcare providers before use.
Cholesterol Management
Foenegriek’s saponin content contributes to its cholesterol-lowering effects. These compounds bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing absorption and promoting excretion. Clinical trials have shown that regular fenugreek consumption can reduce total cholesterol levels by 7-33% and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol by 10-25%.
The seeds’ high fiber content also plays a role in cholesterol management by promoting the production of bile acids, which use cholesterol as a building block. This dual mechanism makes foenegriek a valuable ally in cardiovascular health maintenance.
Athletic Performance Enhancement
Emerging research suggests that foenegriek supplementation may benefit athletic performance. The seeds contain compounds that may support testosterone production in men, potentially leading to improved strength and muscle mass when combined with resistance training.
Some studies have also indicated that fenugreek extract can enhance exercise capacity and reduce exercise-induced muscle damage, though more research is needed to fully establish these effects.
Understanding Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While foenegriek is generally safe for most people when used in culinary amounts, higher doses may cause side effects in some individuals. The most common adverse effects include digestive upset, including nausea, stomach cramping, and diarrhea, particularly when first introducing the seeds to your diet.
Some people may experience a maple syrup-like odor in their sweat and urine due to the sotolone content. This effect is harmless but can be concerning if unexpected.
Foenegriek may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners and diabetes medications. The seeds’ blood sugar-lowering effects can enhance the action of diabetes drugs, potentially causing hypoglycemia. Anyone taking medication should consult their healthcare provider before adding fenugreek supplements to their routine.
Pregnant women should avoid fenugreek supplements, as they may stimulate uterine contractions. However, culinary amounts used in cooking are generally considered safe during pregnancy.
People with peanut or chickpea allergies may also be sensitive to fenugreek, as they belong to the same botanical family.
Incorporating Foenegriek Into Your Daily Diet
Adding foenegriek to your meals can be both delicious and beneficial. The seeds can be used whole, ground, or sprouted, each offering different flavors and textures.
Cooking with Whole Seeds
Toast whole fenugreek seeds in a dry pan for 2-3 minutes to enhance their nutty, maple-like flavor. Add them to curries, stews, and vegetable dishes during the early stages of cooking to allow the flavors to develop. They work particularly well in Indian dal preparations and Middle Eastern spice blends.
Ground Fenugreek Powder
Ground foenegriek integrates more easily into dishes and provides a more subtle flavor. Add it to homemade bread, pancakes, or smoothies for a nutritional boost. Start with small amounts (1/4 teaspoon) and gradually increase to taste, as the flavor can be quite strong.
Fenugreek Tea
Steep 1 teaspoon of whole fenugreek seeds in hot water for 10-15 minutes to create a therapeutic tea. Add honey or lemon to improve the somewhat bitter taste. This preparation is particularly popular among nursing mothers seeking to boost milk production.
Sprouted Seeds
Sprouting foenegriek seeds reduces their bitterness while increasing their nutritional availability. Soak the seeds overnight, then keep them moist in a sprouting jar for 2-4 days until small shoots appear. Add these crunchy sprouts to salads, sandwiches, or grain bowls.
Supplement Forms
For those seeking therapeutic doses, fenugreek supplements are available in capsule, powder, and extract forms. Follow manufacturer guidelines and start with lower doses to assess tolerance.
Maximizing Your Foenegriek Experience
Understanding how to select, store, and prepare foenegriek ensures you get the maximum benefit from this remarkable seed. Choose whole seeds over pre-ground powder when possible, as whole seeds retain their potency longer.
Store fenugreek seeds in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Properly stored whole seeds can maintain their quality for up to two years, while ground fenugreek should be used within six months for optimal flavor and potency.
When introducing foenegriek to your diet, start slowly to allow your digestive system to adapt. Begin with 1/4 teaspoon of ground seeds or 1/2 teaspoon of whole seeds daily, gradually increasing the amount as your body adjusts.
Combining fenugreek with other spices can help balance its slightly bitter taste. It pairs well with coriander, cumin, turmeric, and ginger in savory dishes. For sweet applications, cinnamon and cardamom complement fenugreek’s maple-like notes.
Embracing Ancient Wisdom for Modern Wellness
Foenegriek represents a perfect example of how traditional knowledge aligns with modern scientific understanding. This ancient seed offers genuine health benefits backed by rigorous research, making it a valuable addition to contemporary wellness approaches.
Whether you’re drawn to fenugreek for its blood sugar benefits, hoping to support lactation, or simply wanting to explore new flavors, this versatile seed deserves a place in your pantry. Start small, be consistent, and listen to your body as you discover how this time-tested superfood can enhance your health and culinary adventures.
Remember that while foenegriek offers impressive benefits, it works best as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Consider consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the best way to incorporate this powerful seed into your individual wellness plan.