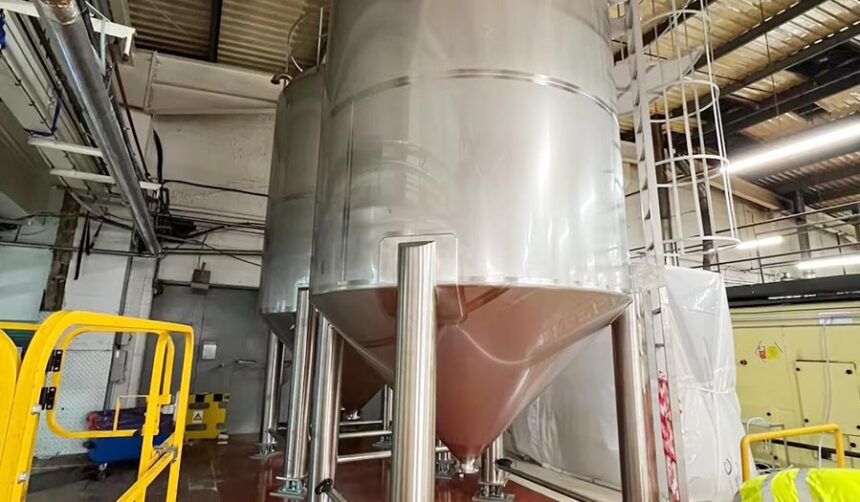
A Practical Buyer’s Guide to Safe, Efficient, and Scalable Food-Grade Tank Solutions
Whether you’re starting a new food business or upgrading an existing facility, selecting the right storage tank is a crucial decision that affects everything from product quality to regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. Food-grade storage tanks serve a wide variety of purposes—from storing raw ingredients and intermediate blends to housing finished products. With so many materials, designs, sizes, and features to choose from, finding the ideal solution can be overwhelming.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the essential considerations when choosing a storage tank for your food processing business, helping you make an informed, future-proof investment.
1. Identify Your Product Type and Processing Needs
Start by clearly understanding what the tank will be used for. Different food products have different storage requirements.
Questions to Ask:
- Is the product solid, liquid, or semi-viscous?
- Is it acidic, salty, or neutral?
- Will it require temperature control?
- Will the tank be part of a CIP (Clean-in-Place) system?
Examples:
- Milk requires sanitary tanks with cooling jackets.
- Chocolate needs heating and mixing capabilities.
- Sauces may require agitation and insulation.
By defining your product’s physical and chemical characteristics, you’ll narrow down the necessary tank specifications.
2. Choose the Right Tank Material
Material selection affects not only product safety but also the longevity and maintenance of your tank.
Common Options:
- 304 Stainless Steel: Suitable for most food applications, resistant to corrosion and easy to clean.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Higher corrosion resistance; ideal for acidic or salty ingredients.
- HDPE or Polypropylene: Acceptable for cold, non-reactive ingredients but not ideal for long-term food contact or high heat.
For nearly all commercial food storage needs, stainless steel is the gold standard due to its durability, hygiene, and compatibility with food safety regulations.
3. Determine the Required Tank Volume and Dimensions
Tank size depends on your batch sizes, production frequency, and available floor space.
Key Considerations:
- Batch vs. continuous production: Larger tanks may be required for high-volume continuous operations.
- Future growth: Always factor in capacity for expansion.
- Space limitations: Consider ceiling height, doorway sizes, and equipment layout.
Tanks are available in sizes ranging from 100L for small operations to 50,000L+ for industrial food plants.
4. Select the Tank Configuration: Vertical or Horizontal
The physical layout and function of your facility will often determine the most suitable tank orientation.
Vertical Tanks:
- Smaller footprint
- Better for gravity drainage
- Easier to insulate or jacket
Horizontal Tanks:
- More stable for mobile setups
- Often used in transport or space-constrained rooms
Conical-bottom tanks are also preferred when complete drainage or ingredient separation is needed.
5. Decide on Temperature Control Features
Many food products must be stored or processed at specific temperatures. Choose tanks that support heating or cooling if necessary.
Temperature Control Options:
- Jacketed tanks for heating/cooling with water, glycol, or steam
- Insulated walls to minimize thermal loss
- Temperature probes and controls for automation and accuracy
Products like dairy, chocolate, soup, and beer all require precise temperature management to maintain quality.
6. Consider Mixing or Agitation Requirements
If your product needs to be blended, emulsified, or kept in suspension, you’ll need a tank with mixing features.
Types of Agitation:
- Low-shear mixers for gentle blending (e.g., milk)
- High-shear agitators for emulsions (e.g., dressings, sauces)
- Scraper blades for sticky or viscous products
- Top or side entry mixers depending on tank geometry
Integrated mixing systems can reduce labor and improve product uniformity.
7. Ensure Sanitary Design and Easy Cleaning
Food-grade tanks must meet strict hygiene standards and allow for fast, thorough cleaning.
Features to Look For:
- Smooth, electropolished interior surfaces
- Minimal welds, crevices, or seams
- Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Steam-in-Place (SIP) compatibility
- Proper drainage angles and bottom outlets
The easier the tank is to clean, the lower the risk of cross-contamination or product spoilage.
8. Evaluate Safety, Accessibility, and User Controls
Safe operation and ease of use are essential for food production environments.
Recommended Features:
- Manways and access ports for inspection
- Non-slip ladders or platforms
- Sight glasses and level indicators
- Digital sensors, gauges, and PLCs for temperature, pressure, and volume monitoring
These features ensure better control, safety, and visibility into your production process.
9. Review Industry Compliance and Certifications
Storage tanks used in food applications must meet specific industry and regional standards.
Certifications to Look For:
- FDA approval for food-contact materials
- 3-A Sanitary Standards (for dairy and beverage)
- EHEDG certification (European markets)
- NSF certification (North America)
Micet tanks, for instance, meet or exceed these standards, ensuring your compliance and peace of mind.
10. Think About Long-Term ROI and Maintenance
Your storage tank should be a long-term asset, not a short-term expense.
Economic Considerations:
- Durability: Stainless steel lasts for decades with minimal maintenance.
- Resale value: Food-grade tanks retain their market value.
- Ease of service: Reliable designs minimize downtime and repair costs.
- Automation: Reduces manual labor and errors
Although premium tanks may cost more upfront, the ROI is strong over time through reduced waste, downtime, and cleaning expenses.
11. Ask About Customization and Turnkey Solutions
Every food business is unique. Partnering with a supplier who offers customization can ensure your tank fits your workflow perfectly.
Customizable Elements:
- Tank size and shape
- Mixing mechanisms
- Port and valve locations
- Sight glasses, level indicators, and automation features
Micet specializes in turnkey stainless steel tank solutions tailored for your product, process, and facility.
Conclusion: Invest in the Right Tank to Scale Your Food Business
Choosing the right food-grade storage tank is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your efficiency, compliance, and product quality. By considering your specific application, material needs, volume requirements, sanitary standards, and temperature or mixing needs, you’ll be well-equipped to make the best choice for your food processing operation.
Micet offers a full range of customizable stainless steel food-grade tanks that meet international hygiene standards and can be configured for virtually any food product or process. Whether you’re storing, mixing, or transporting ingredients, Micet has a tank solution engineered for safety, performance, and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I know what tank size is right for my production volume?
You should base the size on your batch size, frequency of production, and available space. It’s also wise to account for future growth.
2. Can one tank be used for both hot and cold storage?
Yes. Tanks with dual-function jackets and insulation can support both heating and cooling operations.
3. What’s the difference between a storage tank and a mixing tank?
Storage tanks are used to hold product with minimal agitation, while mixing tanks are equipped with agitators or blades to blend ingredients during storage.
Choose Micet for high-quality stainless steel storage tanks built to meet the needs of modern food processing.