As industries strive to meet growing environmental standards and energy efficiency goals, innovative cooling solutions have become paramount. One such solution that has garnered attention in recent years is adiabatic cooling. Unlike traditional air conditioning methods, which often rely on refrigerants and high energy consumption, adiabatic cooling harnesses the natural process of evaporation to lower temperatures effectively. This approach not only minimizes energy costs but also reduces a facility’s carbon footprint.
Imagine an industrial space where the air feels refreshingly cool without the burden of soaring electricity bills or harmful emissions. With adiabatic cooling systems cropping up in commercial settings across various sectors, this vision is becoming a reality. Let’s dive deeper into what makes this technology a game-changer for businesses seeking sustainable climate control solutions while maintaining productivity and comfort.
Understanding Adiabatic Cooling
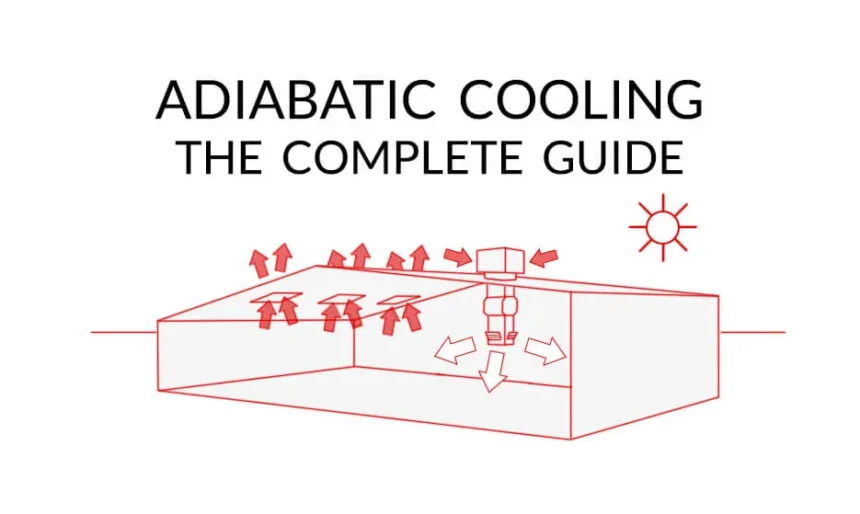
Adiabatic cooling is a process that leverages the principles of thermodynamics to reduce air temperature. At its core, it involves the evaporation of water, which absorbs heat from the surrounding air. This natural phenomenon creates a cooler and more comfortable environment.
In contrast to conventional cooling methods, adiabatic systems do not rely on chemical refrigerants. Instead, they use ambient air and water vapor to cool spaces efficiently.
The beauty of adiabatic cooling lies in its simplicity. When warm air passes over wet surfaces or through evaporative media, moisture evaporates into the airflow. This transition transforms energy from heat into latent energy for evaporation, resulting in significantly lower temperatures without excessive energy expenditure.
This eco-friendly approach makes adiabatic cooling an appealing choice for industries looking to modernize their climate control strategies while prioritizing sustainability and cost savings.
How it Works and its Benefits
Adiabatic cooling harnesses the natural process of evaporation. When water evaporates, it absorbs heat from its surroundings. This phenomenon cools the air without using traditional refrigerants.
The primary benefit is energy efficiency. Adiabatic systems consume significantly less power compared to conventional cooling methods. This translates into lower utility bills for businesses.
Moreover, these systems have a smaller carbon footprint. By relying on water and air instead of harmful chemicals, they promote environmental sustainability.
Another advantage is improved humidity control. Unlike standard air conditioning units that can dry out indoor air, adiabatic cooling maintains optimal moisture levels while still providing effective temperature regulation.
Easy installation adds to its appeal in industrial settings. Many systems are modular and can be integrated into existing infrastructures with minimal disruption to operations.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Adiabatic cooling is revolutionizing how industries manage temperature control. Its applications are diverse, addressing specific needs across various sectors.
In manufacturing plants, this cooling method helps maintain optimal conditions for machinery. It reduces heat buildup and enhances equipment longevity.
Food processing facilities also benefit significantly from adiabatic systems. They ensure perishable goods remain at safe temperatures during production and storage.
Data centers rely on precise temperature management to protect sensitive hardware. Adiabatic cooling provides an efficient solution that minimizes energy consumption while maintaining ideal operational environments.
Moreover, chemical processing sites utilize these systems for safety and efficiency in their processes. By keeping ambient temperatures lower, they help prevent hazardous reactions.
As industries continue to seek sustainable practices, the use of adiabatic cooling continues to grow as a viable option for effective thermal management.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
One remarkable case study comes from a large manufacturing plant in California. Facing soaring energy costs, the facility opted for an adiabatic cooling system. They reported a significant reduction in their operational expenses while maintaining optimal temperatures for equipment.
Another example is found in a food processing company located in Texas. By integrating adiabatic cooling technology, they improved air quality and reduced humidity levels, enhancing product quality and extending shelf life.
A tech firm on the East Coast made the switch as well. Their adiabatic system allowed them to efficiently cool data centers without relying heavily on traditional chillers. This shift led to impressive savings on energy bills and increased reliability during peak demand periods.
Each of these examples highlights how diverse industries can benefit from adopting innovative cooling solutions tailored to their unique needs.
Cost-effectiveness and Energy Efficiency Compared to Traditional Cooling Methods
Adiabatic cooling systems offer significant cost savings over traditional cooling methods. They operate using water evaporation, which uses less energy than conventional air conditioning units. This makes them a compelling choice for businesses looking to reduce their operational expenses.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor. Adiabatic coolers consume much less electricity, translating into lower utility bills. The reduced reliance on electrical power leads to substantial energy conservation.
Moreover, these systems require minimal maintenance and have longer lifespans. Unlike traditional chillers that are prone to wear and tear, adiabatic units tend to be more durable and robust.
For industries facing stringent environmental regulations, adopting adiabatic cooling can significantly decrease the carbon footprint while promoting sustainability practices. Companies not only save money but also align with green initiatives by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy consumption.
Different Types of Adiabatic Cooling Systems
Adiabatic cooling systems come in various types, each designed for specific applications and needs. One popular option is the direct evaporative cooler. This system uses water to cool air directly, making it highly effective in dry climates.
Another type is indirect evaporative cooling. Here, heat exchange occurs between warm and cool air streams without mixing them. This method maintains indoor air quality while efficiently lowering temperatures.
There are also hybrid systems that combine adiabatic cooling with traditional methods like refrigeration. These setups maximize energy savings by using both technologies depending on outdoor conditions.
Cooling towers represent a more industrial approach. They utilize evaporation from water as a means of reducing ambient temperature before circulating cooled air through facilities.
Each system offers unique benefits tailored to different environments, enhancing functionality while promoting energy efficiency in commercial and industrial spaces.
Factors to Consider Before Implementing Adiabatic Cooling
When considering adiabatic cooling for your facility, a few key factors come into play. First, evaluate the local climate. Adiabatic systems work best in dry environments where humidity levels are lower.
Next, analyze your building’s layout. The design influences airflow and cooling efficiency. Ensure that air distribution can be optimized to maximize performance.
Additionally, assess water availability and quality. Adiabatic cooling relies on water vaporization; hence access to clean water is essential for optimal operation.
Don’t overlook regulatory compliance either. Local regulations may impact system installation or usage.
Consider maintenance needs. Regular upkeep ensures long-term performance but adds operational costs. Understanding these elements will help you make an informed decision about adopting adiabatic cooling solutions effectively.
Conclusion: The Future of Cooling Technology in Industrial and Commercial Spaces
The landscape of cooling technology is rapidly evolving. Adiabatic cooling stands out as a promising solution for industrial and commercial spaces. As businesses strive to enhance efficiency while minimizing their environmental impact, adiabatic systems offer an attractive alternative to traditional methods.
With rising energy costs and increasing regulatory pressures regarding sustainability, the shift toward innovative cooling solutions is crucial. Adiabatic systems not only reduce energy consumption but also lower operational costs over time. This positions them as a viable choice for many organizations looking to future-proof their operations.
As awareness grows about the benefits of adiabatic cooling, more industries are likely to explore its potential. The combination of lower carbon footprints and improved performance makes it an appealing option in today’s market. Embracing this technology could significantly transform how facilities manage climate control needs.
Adopting adiabatic cooling is not just about immediate gains; it symbolizes a broader commitment to sustainable practices in industry and commerce alike. The path forward will undoubtedly be shaped by advancements in this area, making it essential for decision-makers to stay informed on developments that could redefine their approach to temperature regulation.