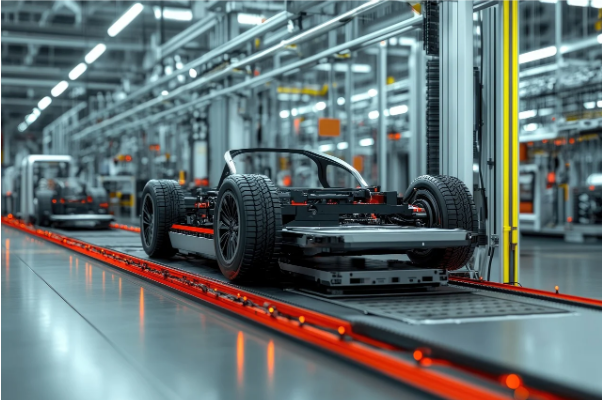
Robots and automated machines are indispensable for several industries, but none is quite like the automotive industry, which uses more robotic solutions than any other. Last year, the automotive sector was responsible for 33 per cent of all industrial robotic installations in the United States. According to recent estimates, 1 million robots were working in the car industry worldwide in the same period.
Most automotive factories use robotic arms like those produced by topautomazioni at every step of the production process. Additionally, there’s an increasing use of collaborative robots, also called “cobots,” that work alongside humans on the factory floor, handling dangerous and physically exhaustive tasks.
This sector is likely to automate its production line even further, pushed by the demand for electric vehicles and a persisting labour shortage. This article will take a closer look at how the automotive industry is using advanced technologies to manufacture vehicles.
Robots Everywhere
Top-notch automakers like Tesla have been investing heavily in the automation of their production lines. Elon Musk said the company plans to cut production costs by half with the help of industrial robots. Even traditional automakers such as Ford use hundreds of these cobots in their factories. Unsurprisingly, market forecasts point to a revenue rise of 4.36 per cent year-to-year until 2028.
Cobots
Collaborative robots were designed to work alongside human workers on the production line without threatening their safety. Cobots can handle several segments of the assembly process and also run quality inspections on assembled parts. These robots are known for considerably speeding up production. The market of automotive cobots is expected to rise more than 26 per cent by 2026.
AMRs
Autonomous mobile robots can move around the factory independently, as the name suggests. They’re built with cameras and sensors for collision detection. Their main tasks are to ensure precision in repetitive processes, reduce labour costs, and guarantee worker safety.
SCARAs
The Selective Compliance Articulated Robotic Arm, or SCARA, performs multiple tasks around a factory, from the warehouse to the assembly line and up to the factory shop.
Six-Axis Robots
Six-axis robots are also common in this industry, handling precision tasks like welding and assembly. These robots have three-dimensional movements and six levels of freedom, allowing them to build car parts accurately and, above all, seamlessly.
Robotic Workforce
Automotive factories mostly use robotic solutions for assembling, machine tending, and quality inspection. They’re also used for joining and welding car parts, painting, and handling hazardous materials while keeping human workers away from accidents. Indeed, every single vehicle today uses some degree of automation in its production.
The automation of the production line brings several benefits for carmakers, workers, and consumers. Robotic solutions deliver more precision, higher quality, and increased safety while also boosting production capacity.
Industrial automation is the way forward to help reduce waste and improve material usage efficiency, saving considerable resources in the long run. Better still, the robots can handle data collection and analysis in tune with the latest advancements of Industry 4.0.