In the world of computing, the need for faster processing, better resource utilization, and improved efficiency is constantly growing. With the increasing complexity of software applications and the rise of data-heavy industries like AI, machine learning, and big data, parallel concurrent processing has emerged as a critical solution to tackle these challenges. But what exactly is parallel concurrent processing, and how does it benefit modern computing?
In this article, we will explore the concepts of parallel processing and concurrent processing, how they differ, and how their combined use in parallel concurrent processing can lead to faster, more efficient computing systems. We will also delve into real-world applications, advantages, challenges, and future trends of this essential technique.
What Is Parallel Concurrent Processing?
Understanding Parallel Processing
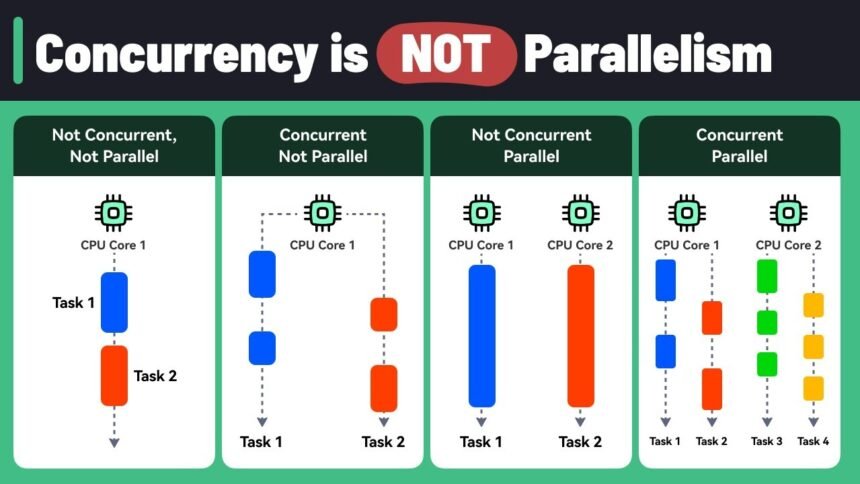
Parallel processing refers to the technique of performing multiple operations or tasks simultaneously. This approach breaks down large problems into smaller sub-tasks that can be solved in parallel, leveraging multiple processors or cores within a computer system. By dividing the workload, parallel processing speeds up computation and increases the efficiency of complex tasks.
There are two primary types of parallel processing:
-
Data Parallelism: The same operation is performed on different pieces of data simultaneously.
-
Task Parallelism: Different tasks or processes run concurrently, each performing different operations at the same time.
Understanding Concurrent Processing
On the other hand, concurrent processing involves running multiple tasks or processes at the same time, but not necessarily simultaneously. Unlike parallel processing, where tasks are truly executed at the same moment, concurrent processing allows tasks to be executed in an interleaved manner, with each task taking turns on a single processor or multiple processors.
The key difference is that concurrency allows for the effective management of several tasks that are in progress at once, while parallelism truly performs multiple operations simultaneously.
Combining the Two: Parallel Concurrent Processing
When you combine parallel processing with concurrent processing, you get parallel concurrent processing. This method allows for multiple tasks to run at the same time and, within each task, the sub-processes to run in parallel. The combination of these two approaches leads to faster processing, improved efficiency, and better use of computing resources.
Why Parallel Concurrent Processing Is Important
The Need for Speed in Modern Computing
With the rapid growth of big data, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and complex scientific simulations, the need for faster computation is more critical than ever. The traditional single-threaded processing is no longer sufficient to handle these computationally intensive tasks.
Parallel concurrent processing enhances performance by allowing systems to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, which is crucial for applications such as:
-
AI and Machine Learning: Training machine learning models with vast amounts of data is time-consuming. Parallel concurrent processing allows for faster model training and real-time predictions.
-
Big Data Analytics: Analyzing massive datasets requires handling multiple queries and computations at once. Parallelism helps divide the workload, allowing data to be processed in parallel across different machines or processors.
-
Scientific Simulations: Research in fields like physics, biology, and climate science often involves solving complex mathematical models that can benefit from parallel computing for faster results.
Maximizing Resource Utilization
Modern processors have multiple cores, and the ability to utilize all available cores is essential for maximizing computational efficiency. Parallel concurrent processing ensures that each core is actively working on a task, which reduces idle time and increases system throughput.
For example, a 16-core processor can handle 16 tasks concurrently, each task running in parallel on different cores, leading to significant performance improvements compared to single-threaded processing.
Real-World Applications of Parallel Concurrent Processing
Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems
Parallel concurrent processing is fundamental to cloud computing, where workloads are distributed across multiple machines. In cloud environments, distributed systems rely on parallel processing techniques to divide tasks across multiple nodes, making applications scalable and capable of handling vast amounts of data.
Services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure use parallel concurrent processing to enable fast data processing and improve the performance of cloud-based applications.
Real-Time Data Processing
Applications requiring real-time data analysis, such as financial trading systems or sensor networks, rely on parallel concurrent processing to handle continuous data streams without delays. For instance, real-time fraud detection algorithms in banking systems use concurrent processing to analyze multiple transactions simultaneously to detect suspicious activity quickly.
Multimedia Processing
Video and image processing are computationally expensive tasks that often require high levels of parallelism. Video rendering, for example, benefits from parallel concurrent processing, where different sections of the video are processed concurrently across multiple cores, leading to faster rendering times.
Similarly, in image recognition tasks used in AI applications, parallel processing can be used to analyze multiple parts of an image simultaneously, speeding up object detection and recognition.
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
In scientific computing, simulations involving large datasets and complex calculations require parallel concurrent processing to achieve reasonable computation times. Supercomputers, which are used for research in areas like weather forecasting, molecular dynamics, and quantum physics, rely on parallel processing across thousands or even millions of cores to complete simulations in a fraction of the time they would take on traditional computers.
The Advantages of Parallel Concurrent Processing
Improved Performance
By leveraging multiple cores and processors, parallel concurrent processing can dramatically speed up computational tasks. This leads to quicker results in data-intensive applications like AI training, video rendering, and scientific simulations.
Scalability
Parallel concurrent processing is highly scalable, allowing systems to handle an increasing amount of work by simply adding more processors or nodes. As data grows and applications require more computing power, parallel processing can easily be scaled to meet those demands.
Resource Efficiency
With parallel concurrent processing, resources such as CPU cores and memory are used more efficiently, ensuring that tasks are completed faster while minimizing system idle time. This also leads to better energy efficiency since multiple cores are actively used rather than running one task sequentially.
Enhanced User Experience
For end-users, parallel concurrent processing translates to faster response times and smoother performance. Applications that perform complex tasks, like real-time analytics, gaming, and media rendering, can offer a better user experience when they are powered by parallel computing technologies.
Challenges in Parallel Concurrent Processing
Complexity of Development
Designing software that can effectively utilize parallel concurrent processing can be challenging. Developers need to break down tasks into smaller sub-tasks that can be executed concurrently while ensuring that the tasks do not interfere with each other. Managing dependencies, synchronization, and handling errors in parallel systems requires advanced programming skills.
Data Dependency and Synchronization
Not all tasks can be easily parallelized. Some tasks depend on the results of others, which can create bottlenecks in parallel systems. Synchronization becomes crucial in these cases to ensure that tasks are executed in the correct order and that data integrity is maintained.
Hardware Limitations
While modern processors have multiple cores, there are limits to how much parallelism can be achieved on a single machine. In some cases, the performance gains from parallel processing may diminish as the number of cores increases, especially if the workload is not optimized for parallel execution.
Overhead Costs
In some cases, managing parallel tasks can introduce additional overhead, especially when tasks need to communicate with each other or share data. This overhead can reduce the overall performance gains from parallel processing if not carefully managed.
The Future of Parallel Concurrent Processing
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents the next frontier in parallel concurrent processing. Quantum computers, leveraging quantum bits (qubits), have the potential to perform multiple calculations simultaneously in ways that classical computers cannot. As quantum technology evolves, it could revolutionize fields like cryptography, machine learning, and complex simulations.
Machine Learning and AI Optimization
As AI models become more complex, parallel concurrent processing will play a crucial role in optimizing the training and inference phases. Distributed deep learning, where parts of a neural network are trained across multiple machines or cores, will continue to advance, leading to faster and more accurate models.
Edge Computing
The rise of edge computing — where processing occurs closer to the data source rather than in a centralized cloud server — will also benefit from parallel concurrent processing. Edge devices, like smartphones and IoT sensors, will rely on parallel computing to process data locally in real-time, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
Conclusion: The Power of Parallel Concurrent Processing
Parallel concurrent processing has become a cornerstone of modern computing, enabling faster, more efficient processing of complex tasks. From powering AI and big data analytics to revolutionizing real-time systems and scientific research, the applications of this technology are vast and growing.
While challenges remain in optimizing parallel concurrent systems, especially regarding development complexity and hardware limitations, the potential benefits — improved performance, scalability, resource efficiency, and enhanced user experience — make it an essential approach for the future of computing.
As technology advances, particularly with developments like quantum computing and edge computing, parallel concurrent processing will continue to evolve, unlocking new possibilities for faster, more efficient computing systems that can handle the demands of tomorrow’s data-driven world.