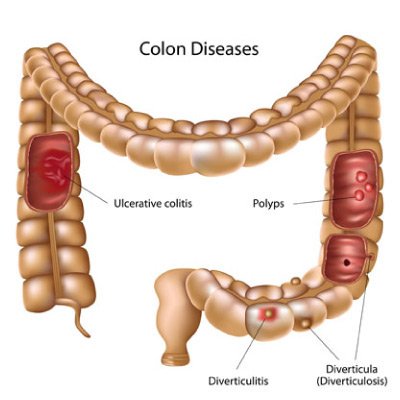
What is Diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is a condition that affects the digestive tract, particularly the colon, where small, bulging pouches, known as diverticula, form in the walls of the intestines. These pouches are common in people over the age of 40 and are usually asymptomatic, but when they become inflamed or infected, it results in diverticulitis. Diverticulitis can cause a variety of symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, fever, nausea, and significant changes in bowel movements. what does poop look like with diverticulitis The most common symptoms include cramping or sharp pain in the lower left side of the abdomen, which is where most diverticula occur. The condition can range from mild to severe and can lead to complications such as abscesses, perforations, or blockages in the colon.
How Diverticulitis Affects Digestive Health
Diverticulitis can significantly disrupt normal digestive functions, leading to various changes in bowel habits. The inflammation and infection caused by diverticulitis can alter the way food moves through the intestines. As a result, stool consistency, frequency, and shape may change. Some individuals may experience constipation, while others may have diarrhea. The colon’s ability to properly absorb nutrients may also be affected, leading to additional symptoms such as bloating, gas, or even rectal bleeding. Understanding these changes is crucial in managing the condition and ensuring prompt treatment. Furthermore, the inflammation in the digestive tract may lead to discomfort and difficulty passing stool, impacting overall quality of life.
Recognizing Changes in Poop with Diverticulitis
What Does Normal Poop Look Like?
Under normal circumstances, healthy stool is brown, soft, and shaped like a log or a smooth cylinder. The consistency should be easy to pass, and it should not cause discomfort or pain during bowel movements. Healthy poop typically has a uniform texture, not too hard or too loose, and should pass regularly without difficulty. The color of normal stool is primarily influenced by bile, which is a digestive fluid produced by the liver and used to break down fats in the intestines.
Common Changes in Poop with Diverticulitis
When diverticulitis occurs, changes in the stool are common and can provide insight into the severity of the condition. Stool may become harder, smaller, or more irregular in shape. The appearance of blood, mucus, or an unusual odor can also indicate the presence of diverticulitis. In some cases, diverticulitis may cause the stool to appear thin, resembling pencil-like shapes. Others may experience very small, pellet-shaped stools due to constipation, while others might experience watery or loose stools, especially if the inflammation affects the colon in a different way. Recognizing these changes early can help in identifying a flare-up and managing the condition before it leads to more serious complications, such as infection or a colon perforation. Monitoring stool changes can be one of the most effective ways to assess how the condition is affecting the digestive system.
Color Changes in Poop Due to Diverticulitis
Bright Red Blood in Stool: Causes and What It Means
The appearance of bright red blood in the stool is one of the most noticeable and concerning signs of diverticulitis. This typically indicates bleeding in the lower portion of the colon or rectum, which can occur if the diverticula become inflamed or infected. Bright red blood may appear on the surface of the stool or be mixed in with the stool itself. While the presence of bright red blood does not necessarily mean there is a severe complication, it is a warning sign that requires prompt attention. In some cases, minor bleeding can occur during a flare-up, but it is important to monitor the amount of blood and seek medical advice if it persists or increases, as it could indicate a more serious condition.
Dark or Black Stool: Is it Serious?
Dark or black stool, which often appears tarry in texture, can be more concerning than bright red blood. This change typically signifies bleeding higher up in the gastrointestinal tract, such as in the stomach or upper part of the small intestine. As blood moves through the digestive tract, it undergoes chemical changes that cause it to appear dark. This is a critical sign of potential internal bleeding, and individuals who notice black, tarry stool should seek immediate medical attention. It is especially important if the stool is accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, or fainting, which could indicate significant blood loss.
Maroon-Colored Stool: What Does It Indicate?
Maroon-colored stool is another common change seen in individuals with diverticulitis. This color of stool generally indicates bleeding from the colon, but it is less severe than black stool. Maroon stool may be a sign that blood is being released from an inflamed or infected diverticulum in the colon. Though this change can often be a sign of a less severe issue, it still warrants medical evaluation. If maroon-colored stool is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, fever, or vomiting, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Shape and Consistency Changes in Diverticulitis Poop
Thin or Pencil-Like Stool
A common sign of diverticulitis is the appearance of thin or pencil-like stool. This change in stool shape often occurs when the colon becomes narrowed due to inflammation from the condition. As the diverticula become inflamed, they can restrict the normal passage of stool, causing it to take on a thinner, more elongated form. Thin stool is typically a sign of some form of obstruction or narrowing in the colon, and while it may not be an immediate emergency, it should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the extent of the inflammation and whether further treatment is needed.
Small and Pellet-Shaped Stool
Small, pellet-like stool is another indicator of constipation, a common symptom of diverticulitis. Inflammation in the colon can slow down the digestive process, leading to harder and smaller stools that are more difficult to pass. Pellet-shaped stool, also known as “rabbit droppings,” can be painful and may require interventions like stool softeners, hydration, or dietary adjustments. If this type of stool persists over several days or weeks, it could lead to further complications, such as impacted stool, which might require medical intervention. Preventing constipation is crucial in managing diverticulitis and avoiding additional flare-ups.
Irregular or Unusual Shapes in Stool
During a diverticulitis flare-up, stool can take on a variety of irregular shapes. Some people may experience segmented or lumpy stool, which indicates inconsistent peristalsis (the wave-like motion of the intestines) due to the inflammation in the digestive tract. Stool may appear jagged or bumpy in texture, which suggests that the movement of food through the colon has been disrupted. This irregularity in stool shape can be uncomfortable and may make bowel movements more difficult. Monitoring these changes is important for understanding the progression of diverticulitis and whether dietary or medical interventions are needed.
Texture and Consistency Variations
Hard, Constipated Poop
Constipation is one of the most common symptoms experienced during a diverticulitis flare-up. As inflammation blocks the normal passage of stool, it can become hard, dry, and difficult to pass. People with diverticulitis often find themselves straining during bowel movements, which can lead to discomfort and potential injury. Hard stools can also exacerbate symptoms of diverticulitis, as increased pressure on the colon may irritate the inflamed diverticula. If constipation persists, it can lead to additional complications such as hemorrhoids or fecal impaction. To manage constipation, it is essential to increase fiber intake, drink plenty of water, and incorporate physical activity to encourage normal bowel movements.
Watery, Loose Stool
On the other hand, some individuals with diverticulitis may experience watery or loose stool, which is a form of diarrhea. This occurs when the inflammation in the colon interferes with its ability to absorb water, leading to stool that is too liquid. Diarrhea can be uncomfortable and cause frequent, urgent bowel movements. It is also possible for loose stool to lead to dehydration, as the body loses fluids more quickly than normal. To manage diarrhea associated with diverticulitis, a person may need to reduce the intake of certain foods that irritate the gut, and medications like anti-diarrheal agents may be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Mucus-Coated Poop: What it Signifies
Mucus in the stool is another common symptom of diverticulitis, often indicating inflammation in the colon. Mucus is a substance produced by the intestines to protect the lining of the digestive tract. When diverticulitis is present, the colon may produce excess mucus as a response to irritation and swelling. This mucus can coat the stool, making it appear slimy or glossy. While mucus alone is not usually a cause for alarm, it is often accompanied by other symptoms of diverticulitis, such as abdominal pain or changes in bowel frequency. If mucus is present with blood or severe symptoms, medical attention should be sought.
6. Odor Changes in Diverticulitis Poop
Why the Smell Might Change
The odor of stool can change dramatically when diverticulitis is present. The smell of normal stool is primarily the result of bacteria in the gut breaking down food. However, when diverticulitis is involved, the infection or inflammation in the colon can alter the balance of bacteria, leading to a more pungent, foul odor. The smell can become stronger and more unpleasant, often indicating bacterial overgrowth or infection. A stronger odor, especially when accompanied by other symptoms like fever or chills, could suggest a more serious infection that requires immediate medical attention.
Is a Stronger Odor a Sign of a Problem?
Yes, a stronger or foul-smelling stool can be a sign that something is wrong, especially if it develops suddenly or during a diverticulitis flare-up. Infected diverticula may cause gas and bacteria to accumulate, which can lead to a particularly offensive odor. If you notice a significant change in the odor of your stool along with other symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, or blood in the stool, it is important to seek medical advice. These symptoms could indicate a worsening of the condition or complications such as an abscess, which may require antibiotic treatment or even surgery.
Frequency of Poop with Diverticulitis
How Often Should You Poop with Diverticulitis?
The frequency of bowel movements can vary greatly for individuals with diverticulitis. Some may experience frequent bowel movements, particularly if they are dealing with diarrhea. Others may struggle with constipation due to the inflammation and infection in the colon. It is common for individuals with diverticulitis to experience irregularity in their bowel habits, including alternating between diarrhea and constipation. Monitoring the frequency and consistency of your stool can provide valuable insights into how the condition is progressing and what does poop look like with diverticulitis the treatment plan is effective.
Impact of Diverticulitis on Bowel Movements
Diverticulitis can make bowel movements more difficult, causing pain and discomfort. Inflammation in the colon may lead to a feeling of incomplete evacuation, bloating, and urgency. Some individuals may also experience a reduced number of bowel movements, particularly if they are dealing with constipation. In cases where diverticulitis leads to an infection or obstruction, it may be difficult to pass stool at all. If you notice any significant changes in the frequency or nature of your bowel movements, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.