In today’s data-driven manufacturing world, success comes down to one thing: visibility. If you can’t see what’s happening on your shop floor in real time, you’re already a step behind. That’s where a production monitoring system comes in.
But installing one isn’t just about buying sensors or software. To make a system work, you need the right plan, setup, training, and follow-through.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to successfully implement a production monitoring system—one that gives you real results, not just fancy dashboards.
What Is a Production Monitoring System?
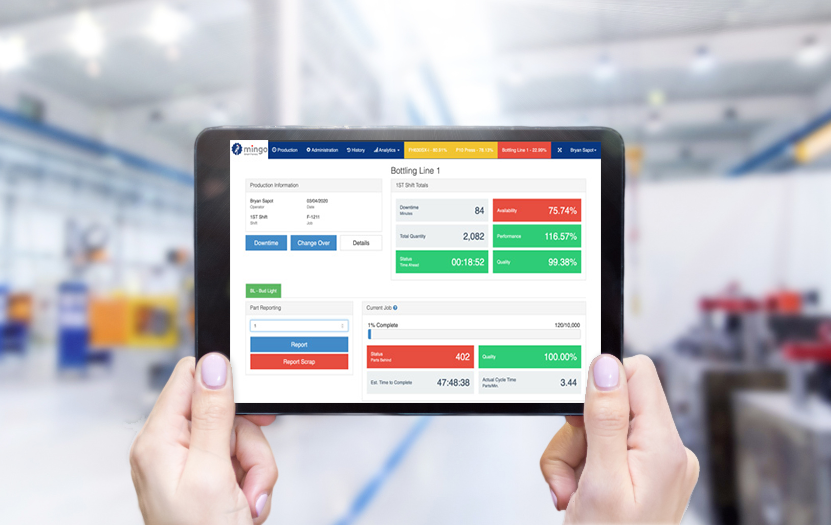
A production monitoring system tracks your manufacturing operations in real time. It collects data from machines, operators, and production lines—like machine uptime, cycle times, output, and defect rates—and shows that data on a dashboard.
The goal? Give you instant visibility, reduce waste, stop downtime before it happens, and improve overall efficiency.
Why Implementation Is So Important
Many companies rush into installing production monitoring tools, only to find their teams don’t use them—or the data isn’t useful. That’s why how you implement the system matters just as much as what system you choose.
A good implementation means:
- Less resistance from your team
- Accurate, real-time data from day one
- A smoother path to higher productivity
Step-by-Step: How to Implement a Production Monitoring System
Let’s break down the process into easy-to-follow steps that work for any size factory.
Step 1: Set Clear Goals
Don’t install technology just to have it. First, define what you want to achieve:
- Do you want to reduce unplanned downtime?
- Are you trying to improve OEE?
- Do you need better shift performance tracking?
Having clear, measurable goals helps guide every step of the setup—and gives you a way to track ROI later.
Step 2: Audit Your Current Setup
Before installing anything, walk through your current operations:
- What machines need monitoring?
- Which processes have the most errors or delays?
- How are you tracking data now (paper, spreadsheets)?
This helps you decide where to start and how to connect the system to your workflow.
Step 3: Choose the Right Technology
The best production monitoring system for you depends on your goals and factory size. Look for:
- Real-time dashboards
- Downtime tracking
- OEE reports
- Alerts and notifications
- Easy integration with your machines or ERP
If your machines are older, choose a system that supports retrofit options (like external sensors or plug-and-play modules).
Step 4: Start With a Small Pilot
Avoid going full scale right away. Instead, pick one line, shift, or department for a pilot test.
Why?
- You can test the system in a real-world environment
- It’s easier to train a small group first
- Early wins create momentum for wider adoption
Use the pilot to work out technical bugs and gather feedback.
Step 5: Install and Connect Equipment
Depending on the system you choose, this may involve:
- Installing sensors to track speed, temperature, vibration, etc.
- Connecting to machine PLCs
- Setting up Wi-Fi or Ethernet networks for data transfer
Make sure all devices are securely mounted, properly powered, and calibrated for accurate readings.
Step 6: Set Up Dashboards and Alerts
Now that data is flowing, configure:
- Live dashboards for operators and managers
- Alerts for downtime, performance drops, or quality issues
- Daily and weekly reports to track KPIs like output, cycle time, and reject rates
Keep visuals simple. Color-coded signals (green for running, red for stopped) are easy to read at a glance.
Step 7: Train Your Team
Your system is only as strong as the people using it. Train everyone who interacts with the system:
- Operators: how to read dashboards and respond to alerts
- Supervisors: how to review reports and adjust schedules
- Maintenance: how to use machine data to prevent breakdowns
Explain not just how, but why the system helps their daily work.
Step 8: Monitor, Improve, and Scale
Once your pilot is running smoothly:
- Review performance weekly
- Look for patterns in machine stoppages or slowdowns
- Involve your team in solving problems
Then scale up! Add more machines or production lines, and expand the dashboards across departments.
You can also integrate the system with your ERP or MES for better planning and reporting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping training: Teams can’t use what they don’t understand.
- Collecting too much data: Focus on what matters to your goals.
- Not acting on insights: Data without action is just noise.
- Rushing full-scale deployment: Take your time to get the foundation right.
Real-World Example
A small metal fabrication company implemented a production monitoring system on one press machine. Within two months, they discovered:
- 30% of downtime was due to material delays
- A night shift had 20% slower cycle times
- Maintenance issues were going unreported
By fixing these problems, they improved output by 18% and used the same system to upgrade their entire facility.
Conclusion: Make It Work for You
A production monitoring system can completely transform how your factory operates—but only if it’s set up the right way.
Start small. Focus on real goals. Train your team. Use the data to take action.
When done right, production monitoring is more than a tool—it becomes the backbone of your continuous improvement process.