Nicotine is a substance that many people encounter, whether through smoking cigarettes, vaping, or using chewing tobacco. For some, it’s a source of comfort; for others, it’s an addiction that can be difficult to shake off. But have you ever wondered how long nicotine actually how long does nicotine stay in your system? This question can hold significance for those looking to quit or even just understand the effects of their habits better.
As our bodies process this potent chemical differently based on various factors, knowing its duration can lead to more informed choices about health and wellness. Let’s dive deeper into the world of nicotine—exploring its effects on the body, what influences its stay in our systems, and ways to break free from its grasp if you’re ready for change. Whether you’re curious about how long you’ll test positive on a drug screen or simply want clarity on your health journey, there’s plenty to uncover here.
Understanding Nicotine and its Effects on the Body
Nicotine is a powerful stimulant found in tobacco products. When inhaled or ingested, it rapidly enters the bloodstream and reaches the brain within seconds. This quick delivery system contributes to its addictive nature.
Once in the brain, nicotine binds to receptors that release neurotransmitters like dopamine, which creates feelings of pleasure and reward. This pleasurable experience can lead users to crave more nicotine over time.
Physiologically, nicotine increases heart rate and blood pressure while affecting hormone levels. It also stimulates adrenaline production, leading to heightened alertness but often masking fatigue.
Long-term use can alter brain chemistry, making it challenging for smokers or users of other forms of nicotine to quit without experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Understanding these effects underscores why many find breaking free from this substance so difficult yet vital for overall health and well-being.
Factors Affecting How Long Nicotine Stays in the System
Several factors influence how long nicotine lingers in your body. One major element is individual metabolism. People metabolize substances at different rates, which can significantly affect nicotine clearance.
Another contributing factor is frequency of use. Regular smokers may find that nicotine stays longer compared to occasional users. The more often you consume it, the more time your body needs to process and eliminate it.
Hydration levels play a crucial role as well. Staying well-hydrated can help speed up the detoxification process, while dehydration might prolong it.
Genetics also come into play. Some individuals have genetic variations that impact how quickly their bodies break down nicotine.
Age and overall health status are relevant too. Younger individuals with better metabolic rates generally clear substances faster than older adults or those with underlying health issues.
The Duration of Nicotine in Different Forms (Cigarettes, Vapes, Chewing Tobacco)
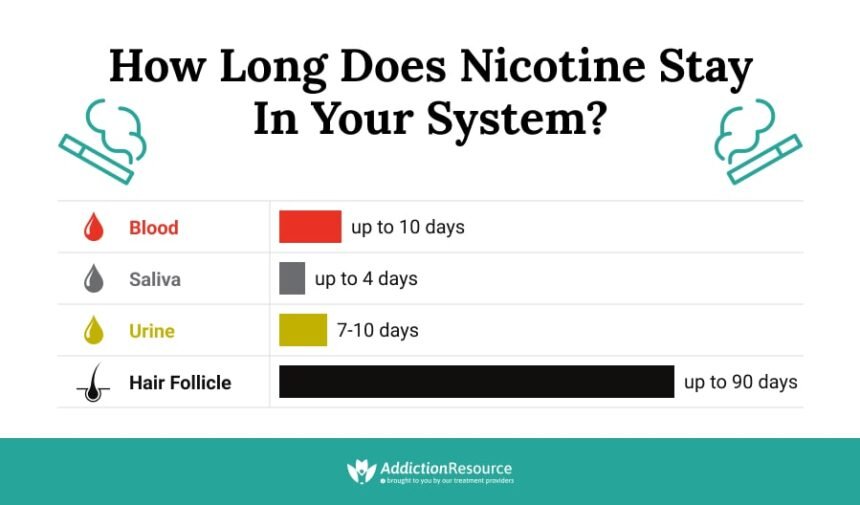
Nicotine can linger in the body for various durations depending on its form. Cigarettes typically release nicotine rapidly, with traces detectable within 1 to 3 days after use. The quick absorption means that smokers might experience withdrawal symptoms sooner.
Vaping has gained popularity, but it also introduces nicotine into the system swiftly. Depending on the device and liquid concentration, nicotine from vapes may stay in your body for up to 5 days.
Chewing tobacco presents another scenario entirely. This form of nicotine enters the bloodstream more slowly, resulting in a longer presence—often extending beyond a week or more due to prolonged exposure during usage.
Each method not only affects how long nicotine remains but also influences withdrawal experiences differently for users.
Health Risks Associated with Prolonged Nicotine Use
Prolonged nicotine use poses significant health risks that can affect nearly every system in the body. It is well-known for its addictive nature, making it difficult for users to quit. This dependency can lead to increased consumption and greater exposure to harmful substances.
One of the most alarming effects is cardiovascular disease. Nicotine raises heart rate and blood pressure, contributing to a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes. The strain on blood vessels can initiate long-term damage over time.
Respiratory complications are also common among chronic users. Whether from smoking or vaping, nicotine irritates airways and lungs, leading to conditions like chronic bronchitis or emphysema.
Additionally, prolonged nicotine intake has been linked to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. The cycle of addiction often exacerbates these conditions, creating a challenging situation for many individuals seeking relief through substance use rather than healthy coping mechanisms.
Tips for Quitting Nicotine
Quitting nicotine can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it’s entirely achievable. Start by setting a clear quit date. This gives you time to prepare mentally and physically.
Find a support system—friends, family, or online communities can provide encouragement. Sharing your journey makes it feel less isolating.
Consider using nicotine replacement therapies like patches or gum. They can help ease withdrawal symptoms without the harmful effects of smoking.
Stay busy! Engage in activities that keep your mind off cravings. Exercise is particularly effective; it boosts mood and reduces stress.
Identify triggers that make you want to use nicotine and develop coping mechanisms for these situations. Whether it’s deep breathing exercises or going for a walk, having a plan helps.
Reward yourself for milestones along the way. Celebrate each day without nicotine as an achievement worth recognizing.
Natural Ways to Detoxify Your Body from Nicotine
Detoxifying your body from nicotine can be a refreshing journey. Start by hydrating. Water flushes out toxins and keeps you feeling energized.
Incorporating fresh fruits and vegetables can also help. Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, support cellular repair and boost immunity.
Herbal teas are another excellent option. Chamomile or green tea can soothe the digestive system while promoting detoxification.
Regular exercise is crucial too. Physical activity increases circulation, helping to eliminate substances more efficiently through sweat.
Consider breathing exercises or meditation. Stress reduction plays a significant role in supporting your body’s natural ability to heal itself after quitting nicotine.
Conclusion
Understanding how long does nicotine stay in your system is essential for anyone dealing with nicotine use, whether from smoking cigarettes, vaping, or chewing tobacco. The effects of nicotine can linger in the body longer than many expect. Individual factors like metabolism and frequency of use play significant roles in determining this duration.
Each form of nicotine has its own timeline. Cigarettes may clear out faster compared to vapes and smokeless options, which could lead to prolonged exposure due to different absorption rates. Recognizing these differences helps users make informed choices.
Prolonged use can also lead to various health risks that affect both mental and physical well-being. It’s vital to be aware of these dangers while considering quitting strategies. Whether it’s relying on support systems or exploring natural detox methods, taking steps towards cessation can vastly improve quality of life.
Understanding the intricacies around nicotine’s presence in our bodies empowers individuals toward healthier decisions moving forward.