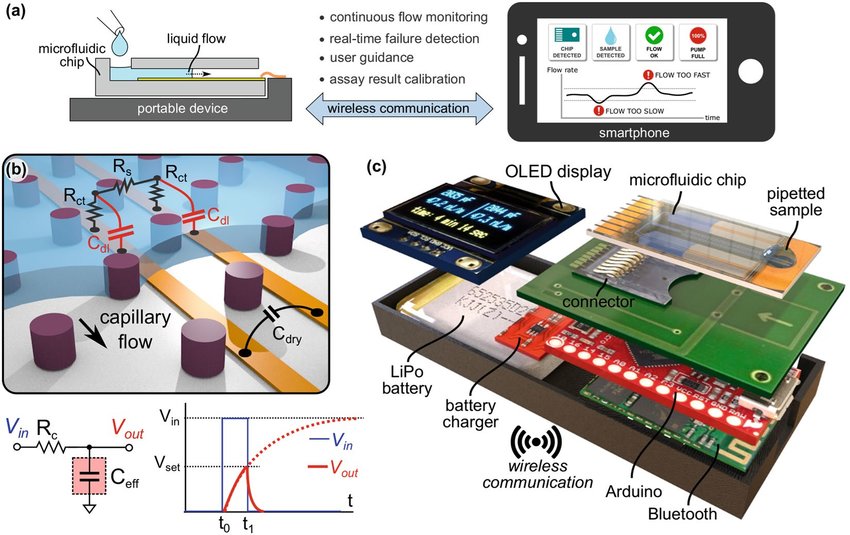
Imagine a world where the boundaries between fluid mechanics and electronic storage blur. This is not just a futuristic vision; it’s happening now with the emergence of microfluidic capacitors. These innovative devices harness the power of liquids to store electrical energy, creating exciting possibilities in various fields. As technology evolves, understanding how these miniature marvels work can open doors to new applications and advancements.
Microfluidic capacitors represent a fascinating intersection of engineering disciplines, merging principles from both fluid dynamics and electronics. With their ability to manipulate tiny volumes of liquid for energy storage, they are poised to revolutionize industries ranging from biotechnology to renewable energy. Join us as we dive deeper into this cutting-edge technology and explore its transformative potential across multiple sectors.
Understanding Fluid Mechanics and Electronic Storage
Fluid mechanics is the study of how fluids behave in motion and at rest. It explores the forces acting on liquids and gases, revealing insights into their interactions with solid surfaces. This field plays a crucial role in various engineering applications, from designing pipelines to understanding airflow over wings.
On the other hand, electronic storage revolves around capturing and retaining data using electrical systems. Traditional capacitors store electrical energy through static charge separation, which has proven efficient yet limited in certain contexts.
Microfluidic capacitors merge these two domains by utilizing fluid dynamics to enhance energy storage capabilities. By manipulating fluid flow within micro-scale channels, they create innovative mechanisms for charge accumulation that traditional systems cannot achieve alone. This intersection opens new avenues for compact energy solutions while pushing boundaries in both fluid mechanics and electronics.
How Microfluidic Capacitors Work
Microfluidic capacitors operate by utilizing the dynamics of fluid flow combined with electrical principles. At their core, these devices manage tiny volumes of liquid within microchannels, allowing for precise control over charge storage.
When an electric field is applied, ions from the liquid move towards electrodes embedded in the device. This movement creates a separation of charges, effectively storing energy as electrostatic potential.
The unique design allows for rapid response times and high efficiency. The small scale enhances interactions between fluid mechanics and electrostatics, enabling quick charging and discharging cycles.
Key to this technology is the manipulation of fluids at microscopic levels. This results in a highly compact solution that stands out compared to traditional capacitors. By bridging two distinct fields—fluid dynamics and electronics—microfluidic capacitors pave new pathways for innovative applications across various sectors.
Advantages of Using Microfluidic Capacitors
Microfluidic capacitors offer several unique advantages over traditional electronic storage systems. Their compact size allows for integration into various devices without occupying excessive space.
One significant benefit is their ability to handle varied fluid dynamics. This versatility means they can be tailored for specific applications, enhancing performance in diverse environments.
Additionally, microfluidic capacitors exhibit rapid charge and discharge times. This efficiency enables faster processing speeds, which is crucial in high-demand settings like data centers or advanced computing systems.
Their energy-efficient nature contributes to reduced power consumption. As industries strive for sustainability, this feature aligns perfectly with modern eco-friendly initiatives.
Moreover, the use of liquid electrolytes enhances safety by minimizing risks associated with overheating or chemical leaks often seen in conventional batteries.
The innovative design also promotes scalability, making it easier to produce them at larger volumes while maintaining quality and reliability.
Applications in Various Industries
Microfluidic capacitors are making waves across multiple sectors. In the healthcare realm, they enable precise drug delivery systems. These devices can control the flow of medications at a micro-level, enhancing patient outcomes.
The automotive industry also benefits from this technology. Microfluidic capacitors optimize fuel mixing in combustion engines, leading to improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
In electronics, they play a crucial role in energy storage solutions. Their compact size allows for innovative designs in wearable tech and portable devices without sacrificing performance.
Environmental monitoring is another area where these capacitors shine. They enhance sensors that detect pollutants or contaminants in water sources, ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.
Research labs utilize microfluidic capacitors to streamline experiments involving fluid dynamics and chemical reactions. This flexibility promotes faster innovation cycles across various scientific fields.
Current Research and Development
Current research into microfluidic capacitors is vibrant and multifaceted. Scientists and engineers are exploring various materials to enhance performance and efficiency. Innovations in nanomaterials promise superior conductivity, leading to improved energy storage capabilities.
Collaboration between academic institutions and industry leaders is accelerating advancements. Researchers focus on integrating these capacitors into existing electronic systems, paving the way for more compact devices.
Prototypes are being tested under varying conditions to assess reliability and durability. This iterative process allows for fine-tuning designs based on real-world applications.
Moreover, interdisciplinary studies are emerging that merge fluid dynamics with advanced circuitry design. These approaches aim to create hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of both fields.
As funding increases, so does the potential for breakthroughs that could revolutionize how we think about energy storage in micro-scale environments. The excitement surrounding these developments keeps pushing boundaries further than ever before.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Microfluidic capacitors face several challenges that can impact their widespread adoption. One significant hurdle is the integration of these devices into existing electronic systems. Compatibility with current manufacturing processes must be ensured to facilitate a smooth transition.
Another challenge lies in material selection. Identifying substances that maintain efficiency while being cost-effective is crucial for commercial viability. Researchers are exploring innovative materials but still encounter limitations in performance.
Moreover, scalability presents its own set of difficulties. While prototypes may function well at small scales, replicating this success in mass production remains complex.
Looking ahead, advancements in nanotechnology and materials science hold promise for overcoming these obstacles. As research progresses, we may witness breakthroughs that enhance performance and reduce costs significantly.
The future for microfluidic capacitors seems bright as industries explore new applications and functionalities. With continued innovation, they could revolutionize how we think about energy storage and fluid dynamics together.
Conclusion
Microfluidic capacitors represent an exciting convergence of fluid mechanics and electronic storage. As technology evolves, these innovative devices show promise in enhancing efficiency across numerous industries. With their unique ability to leverage the properties of fluids for energy storage, microfluidic capacitors could redefine our approach to electronics.
The advantages they offer—like compact size, high energy density, and faster charging times—make them a compelling alternative to traditional methods. Their potential applications extend from medical devices to renewable energy systems, highlighting their versatility.
Current research continues to push boundaries in this field. Scientists are exploring new materials and designs that can further improve performance while overcoming existing challenges such as scalability and integration with current technologies.
As advancements unfold, the future of microfluidic capacitors looks promising. They may well become essential components in next-generation electronic systems where efficiency is paramount. The continuous exploration in this area opens up myriad possibilities that could transform how we store and utilize energy moving forward.